Augmented Reality

Augmented reality (AR) is an interactive experience of a real-world environment where the objects that reside in the real world are enhanced by computer-generated perceptual information, sometimes across multiple sensory modalities, including visual, auditory, haptic, somatosensory and olfactory.
Emerging Technology:

Augmented Reality is relatively new, and its support in FME is still at a very early stage, but its being rapidly developed and implemented by technology giants like Google and Apple so its becoming more mainstream.
Lidar Scanner on Your Mobile Device!
Apple is bringing Lidar scanners to the iPad and probably the iPhone that can capture an environment in 3D but also use that information to better place objects in to that scene.
Google Maps Mobile now can do augmented reality directions by scanning your location and then superimposing your route into the augmented view.
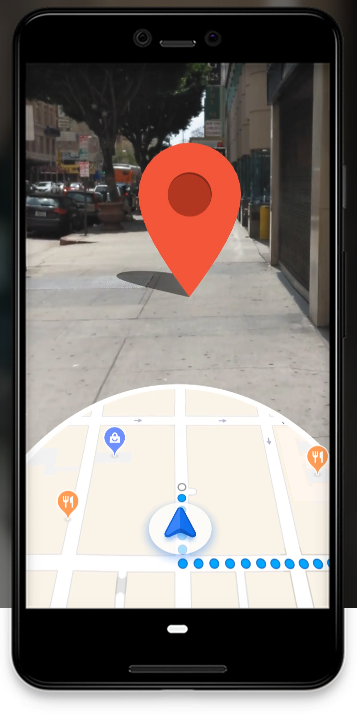
GeoSpatial is at the heart of AR:
Wether its consumer navigation or field workers augmented reality is about placing objects in the real world and is therefore inherently spatial. It becomes another tool for visualising the spatial data that we've collected, created and managed for as long as people having been making maps. Its just a new way of presenting that data that allows it to be more easily understood and placed in context.
FME and AR:
With the FME Mobile Apps for Augmented Reality and processing data, you can explore your data in whole new ways and in virtually any location. Use FME AR to transport to Mars, or keep your application practical and view directional signage, underground assets, and city infrastructure. When you combine FME AR with FME Workbench, your data's only limit is your own imagination.
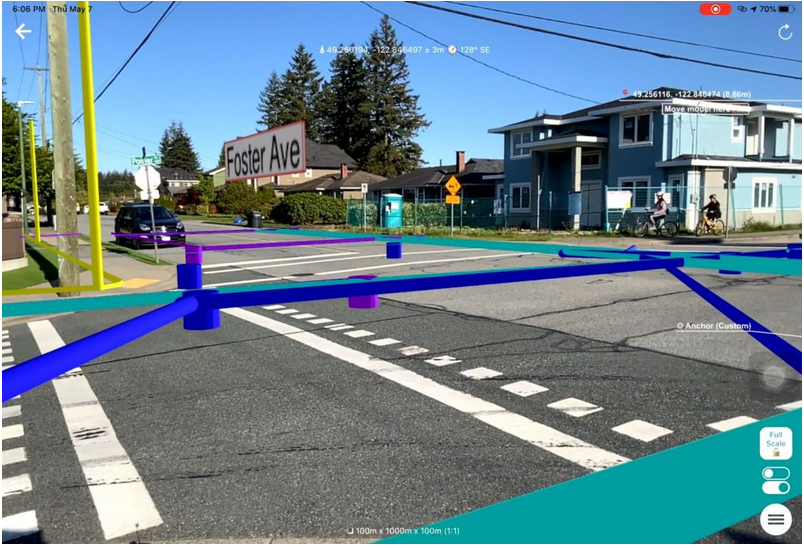

Indoor Way-finding:
We can merge our indoor building plans, and indoor data formats and present a new way of "following the blue dot" around those environments.
FME and Field Workers:
Augmented reality shows workers the information they need and is improving the experience for mobile workers. Field technicians can now point a mobile device at an asset and get real-time diagnostic information as well as service guidance on their screens. For example, mobile workers servicing photocopiers can’t possibly know the nuances of every single model. By using an AR tool to scan a barcode, they can quickly learn about the model and obtain instructions to solve a particular problem — and those instructions are actually overlaid on the picture of the photocopier, arming them with all the information they need on one screen to solve the problem. AR also enables the mobile worker to collaborate with remote colleagues while they share the same visual of the problem at hand.
Placing Utilities in front of field teams so they can better visualise where buried assets are located for example.
Immersive Environments:
Use AR to visualise 3D environments and create an immersive experience of historical buildings, or sites.
Visualise Lidar Scans:
Recreate historic environments in AR for visitors
Add recreations of historic buildings or sites and visitors can add these into the real world setting to better aid with understanding that environment or allow planners and site managers to better manage a site.